boost::random::hyperexponential_distribution
// In header: <boost/random/hyperexponential_distribution.hpp> template<typename RealT = double> class hyperexponential_distribution { public: // types typedef RealT result_type; typedef RealT input_type; // member classes/structs/unions class param_type { public: // types typedef hyperexponential_distribution distribution_type; // public member functions param_type(); template<typename ProbIterT, typename RateIterT> param_type(ProbIterT, ProbIterT, RateIterT, RateIterT); template<typename ProbRangeT, typename RateRangeT> param_type(ProbRangeT const &, RateRangeT const &, typename boost::disable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< ProbRangeT >::value||boost::has_pre_increment< RateRangeT >::value >::type * = 0); template<typename RateIterT> param_type(RateIterT, RateIterT, typename boost::enable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< RateIterT >::value >::type * = 0); template<typename RateRangeT> param_type(RateRangeT const &); param_type(std::initializer_list< RealT >, std::initializer_list< RealT >); param_type(std::initializer_list< RealT >); std::vector< RealT > probabilities() const; std::vector< RealT > rates() const; // friend functions template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > & operator<<(std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > &, const param_type &); template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > & operator>>(std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > &, const param_type &); bool operator==(const param_type &, const param_type &); bool operator!=(const param_type &, const param_type &); }; // public member functions hyperexponential_distribution(); template<typename ProbIterT, typename RateIterT> hyperexponential_distribution(ProbIterT, ProbIterT, RateIterT, RateIterT); template<typename ProbRangeT, typename RateRangeT> hyperexponential_distribution(ProbRangeT const &, RateRangeT const &, typename boost::disable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< ProbRangeT >::value||boost::has_pre_increment< RateRangeT >::value >::type * = 0); template<typename RateIterT> hyperexponential_distribution(RateIterT, RateIterT, typename boost::enable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< RateIterT >::value >::type * = 0); template<typename RateRangeT> hyperexponential_distribution(RateRangeT const &); explicit hyperexponential_distribution(param_type const &); hyperexponential_distribution(std::initializer_list< RealT > const &, std::initializer_list< RealT > const &); hyperexponential_distribution(std::initializer_list< RealT > const &); template<typename URNG> RealT operator()(URNG &) const; template<typename URNG> RealT operator()(URNG &, const param_type &) const; std::size_t num_phases() const; std::vector< RealT > probabilities() const; std::vector< RealT > rates() const; RealT min() const; RealT max() const; param_type param() const; void param(param_type const &); void reset(); // friend functions template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > & operator<<(std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > &, const hyperexponential_distribution &); template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > & operator>>(std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > &, const hyperexponential_distribution &); bool operator==(const hyperexponential_distribution &, const hyperexponential_distribution &); bool operator!=(const hyperexponential_distribution &, const hyperexponential_distribution &); };
超指数分布是一个实值连续分布,有两个参数:阶段概率向量 probs 和速率向量 rates。
一个 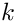 -阶段的超指数分布是
-阶段的超指数分布是 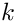 个指数分布的混合。因此,它也被称为混合指数分布或并行
个指数分布的混合。因此,它也被称为混合指数分布或并行 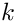 -阶段指数分布。
-阶段指数分布。
一个 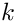 -阶段的超指数分布由两个参数表征,即阶段概率向量
-阶段的超指数分布由两个参数表征,即阶段概率向量 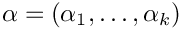 和速率向量
和速率向量 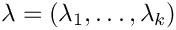 。
。
一个 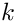 -阶段的超指数分布常用于排队论中,以模拟
-阶段的超指数分布常用于排队论中,以模拟 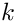 个独立事件的叠加分布。例如,一个具有
个独立事件的叠加分布。例如,一个具有 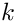 个并行服务器的排队站的服务时间分布,其中第
个并行服务器的排队站的服务时间分布,其中第 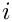 个服务器以概率
个服务器以概率 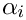 被选中,其服务时间分布为速率为
被选中,其服务时间分布为速率为 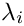 的指数分布(Allen,1990; Papadopolous et al.,1993; Trivedi,2002)。
的指数分布(Allen,1990; Papadopolous et al.,1993; Trivedi,2002)。
例如,计算系统中的 CPU 服务时间分布通常表现出这种分布(Rosin,1965)。此外,不同类型客户到达单个排队站的到达过程通常被建模为超指数分布(Papadopolous et al.,1993)。类似地,如果一个产品在多个并行装配线上制造,并且输出被合并,那么整个产品的故障密度很可能是超指数的(Trivedi,2002)。
最后,由于超指数分布表现出较高的变异系数(CoV),即 CoV > 1,因此它特别适合拟合具有大 CoV 的经验数据(Feitelson,2014; Wolski et al.,2013),并且可以近似长尾概率分布(Feldmann et al.,1998)。
有关更多信息和示例,请参见(Boost,2014)。
一个 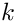 -阶段的超指数分布具有概率密度函数
-阶段的超指数分布具有概率密度函数
其中
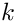 是阶段数,也是输入向量参数的大小,
是阶段数,也是输入向量参数的大小,
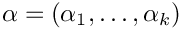 是阶段概率向量参数,
是阶段概率向量参数,
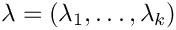 是速率向量参数。
是速率向量参数。
给定一个具有阶段概率向量 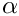 和速率向量
和速率向量 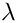 的
的 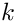 -阶段超指数分布,随机变量生成算法包括以下步骤(Tyszer,1999):
-阶段超指数分布,随机变量生成算法包括以下步骤(Tyszer,1999):
生成一个在区间 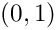 上均匀分布的随机变量
上均匀分布的随机变量 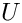 。
。
使用 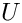 选择适当的
选择适当的 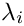 (例如,可以使用别名法来完成此步骤)。
(例如,可以使用别名法来完成此步骤)。
生成一个具有速率参数 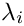 的指数分布随机变量
的指数分布随机变量 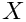 。
。
返回 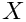 。
。
参考文献
A.O. Allen, Probability, Statistics, and Queuing Theory with Computer Science Applications, Second Edition, Academic Press, 1990。
Boost C++ Libraries, Boost.Math / Statistical Distributions: Hyperexponential Distribution, Online: https://boost.ac.cn/doc/libs/release/libs/math/doc/html/dist.html , 2014。
D.G. Feitelson, Workload Modeling for Computer Systems Performance Evaluation, Cambridge University Press, 2014
A. Feldmann and W. Whitt, Fitting mixtures of exponentials to long-tail distributions to analyze network performance models, Performance Evaluation 31(3-4):245, doi:10.1016/S0166-5316(97)00003-5, 1998。
H.T. Papadopolous, C. Heavey and J. Browne, Queueing Theory in Manufacturing Systems Analysis and Design, Chapman & Hall/CRC, 1993, p. 35。
R.F. Rosin, Determining a computing center environment, Communications of the ACM 8(7):463-468, 1965。
K.S. Trivedi, Probability and Statistics with Reliability, Queueing, and Computer Science Applications, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2002。
J. Tyszer, Object-Oriented Computer Simulation of Discrete-Event Systems, Springer, 1999。
Wikipedia, Hyperexponential Distribution, Online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperexponential_distribution , 2014。
Wolfram Mathematica, Hyperexponential Distribution, Online: http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HyperexponentialDistribution.html , 2014。
Marco Guazzone (marco.guazzone@gmail.com)
hyperexponential_distribution 公有成员函数hyperexponential_distribution();
构造一个 1-阶段的 hyperexponential_distribution(即指数分布),速率为 1。
template<typename ProbIterT, typename RateIterT> hyperexponential_distribution(ProbIterT prob_first, ProbIterT prob_last, RateIterT rate_first, RateIterT rate_last);
从分布的阶段概率向量和速率向量参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution。
阶段概率向量参数由范围 [prob_first, prob_last) 的迭代器对定义,而速率向量参数由范围 [rate_first, rate_last) 的迭代器对定义。
参考文献
ISO, ISO/IEC 14882-2014: Information technology - Programming languages - C++, 2014
参数 |
|
||||||||
模板参数 |
|
template<typename ProbRangeT, typename RateRangeT> hyperexponential_distribution(ProbRangeT const & prob_range, RateRangeT const & rate_range, typename boost::disable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< ProbRangeT >::value||boost::has_pre_increment< RateRangeT >::value >::type * = 0);
从分布的阶段概率向量和速率向量参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution。
阶段概率向量参数由范围 prob_range 定义,而速率向量参数由范围 rate_range 定义。
![[Note]](../../../../doc/src/images/note.png) |
注意 |
|---|---|
最后一个 |
template<typename RateIterT> hyperexponential_distribution(RateIterT rate_first, RateIterT rate_last, typename boost::enable_if_c< boost::has_pre_increment< RateIterT >::value >::type * = 0);
从分布的速率向量参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution,并具有相等的阶段概率。
速率向量参数由范围 [rate_first, rate_last) 的迭代器对定义,而阶段概率向量参数设置为相等的阶段概率(即,一个长度与速率向量相同的向量,其每个元素设置为 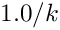 )。
)。
![[Note]](../../../../doc/src/images/note.png) |
注意 |
|---|---|
最后一个 |
参考文献
ISO, ISO/IEC 14882-2014: Information technology - Programming languages - C++, 2014
参数 |
|
||||
模板参数 |
|
template<typename RateRangeT> hyperexponential_distribution(RateRangeT const & rate_range);
从分布的“速率”参数构造一个 param_type,并具有相等的阶段概率。
速率向量参数由范围 rate_range 定义,而阶段概率向量参数设置为相等的阶段概率(即,一个长度与速率向量相同的向量,其每个元素设置为 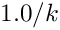 )。
)。
参数 |
|
||
模板参数 |
|
explicit hyperexponential_distribution(param_type const & param);
从其参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution。
参数 |
|
hyperexponential_distribution(std::initializer_list< RealT > const & l1, std::initializer_list< RealT > const & l2);
从分布的阶段概率向量和速率向量参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution。
阶段概率向量参数由 brace-init-list(ISO,2014,sec. 8.5.4 [dcl.init.list]) l1 定义,而速率向量参数由 brace-init-list(ISO,2014,sec. 8.5.4 [dcl.init.list]) l2 定义。
参考文献
ISO, ISO/IEC 14882-2014: Information technology - Programming languages - C++, 2014
参数 |
|
hyperexponential_distribution(std::initializer_list< RealT > const & l1);
从分布的速率向量参数构造一个 hyperexponential_distribution,并具有相等的阶段概率。
速率向量参数由 brace-init-list(ISO,2014,sec. 8.5.4 [dcl.init.list]) l1 定义,而阶段概率向量参数设置为相等的阶段概率(即,一个长度与速率向量相同的向量,其每个元素设置为 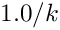 )。
)。
参考文献
ISO, ISO/IEC 14882-2014: Information technology - Programming languages - C++, 2014
参数 |
|
template<typename URNG> RealT operator()(URNG & urng) const;
获取一个按照超指数分布的随机变量。
参数 |
|
||
模板参数 |
|
||
返回 |
一个按照超指数分布的随机变量。 |
template<typename URNG> RealT operator()(URNG & urng, const param_type & param) const;
获取一个按照超指数分布且其参数由 param 指定的随机变量。
参数 |
|
||||
模板参数 |
|
||||
返回 |
一个按照超指数分布且其参数由 |
std::size_t num_phases() const;
返回分布的阶段数。
std::vector< RealT > probabilities() const;
返回分布的阶段概率向量参数。
std::vector< RealT > rates() const;
返回分布的速率向量参数。
RealT min() const;
返回分布可以产生的最小值。
RealT max() const;
返回分布可以产生的最大值。
param_type param() const;
返回分布的参数。
void param(param_type const & param);
设置分布的参数。
void reset();
效果:随后的分布使用不依赖于调用 reset 之前的任何引擎生成的值。
hyperexponential_distribution 友元函数template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > & operator<<(std::basic_ostream< CharT, Traits > & os, const hyperexponential_distribution & hd);
将一个 hyperexponential_distribution 写入一个 std::ostream。
template<typename CharT, typename Traits> std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > & operator>>(std::basic_istream< CharT, Traits > & is, const hyperexponential_distribution & hd);
从一个 std::istream 读取一个 hyperexponential_distribution。
bool operator==(const hyperexponential_distribution & lhs, const hyperexponential_distribution & rhs);
如果两个 hyperexponential_distribution 实例在给定相同的生成器时将返回相同的数值序列,则返回 true。
bool operator!=(const hyperexponential_distribution & lhs, const hyperexponential_distribution & rhs);
如果两个 hyperexponential_distribution 实例在给定相同的生成器时将返回不同的数值序列,则返回 true。